Google ranking factors from the Yandex source code leak
This article was formerly a presentation from the March Hawke’s Bay Digital Marketing Meetup
The Yandex Search Engine Source Code Leak and Its Impact on Google SEO
The source code of Yandex, the fourth most popular search engine, was leaked online.
Yandex is commonly understood to be the closest search engine in terms of functionality to Google, meaning that the source code leak has led to a surge of interest among SEO experts.
We’ve reverse-engineered the source code to understand what ranking factors affect the Yandex search engine and which one’s we believe that we can use Google SEO.
What is Yandex?
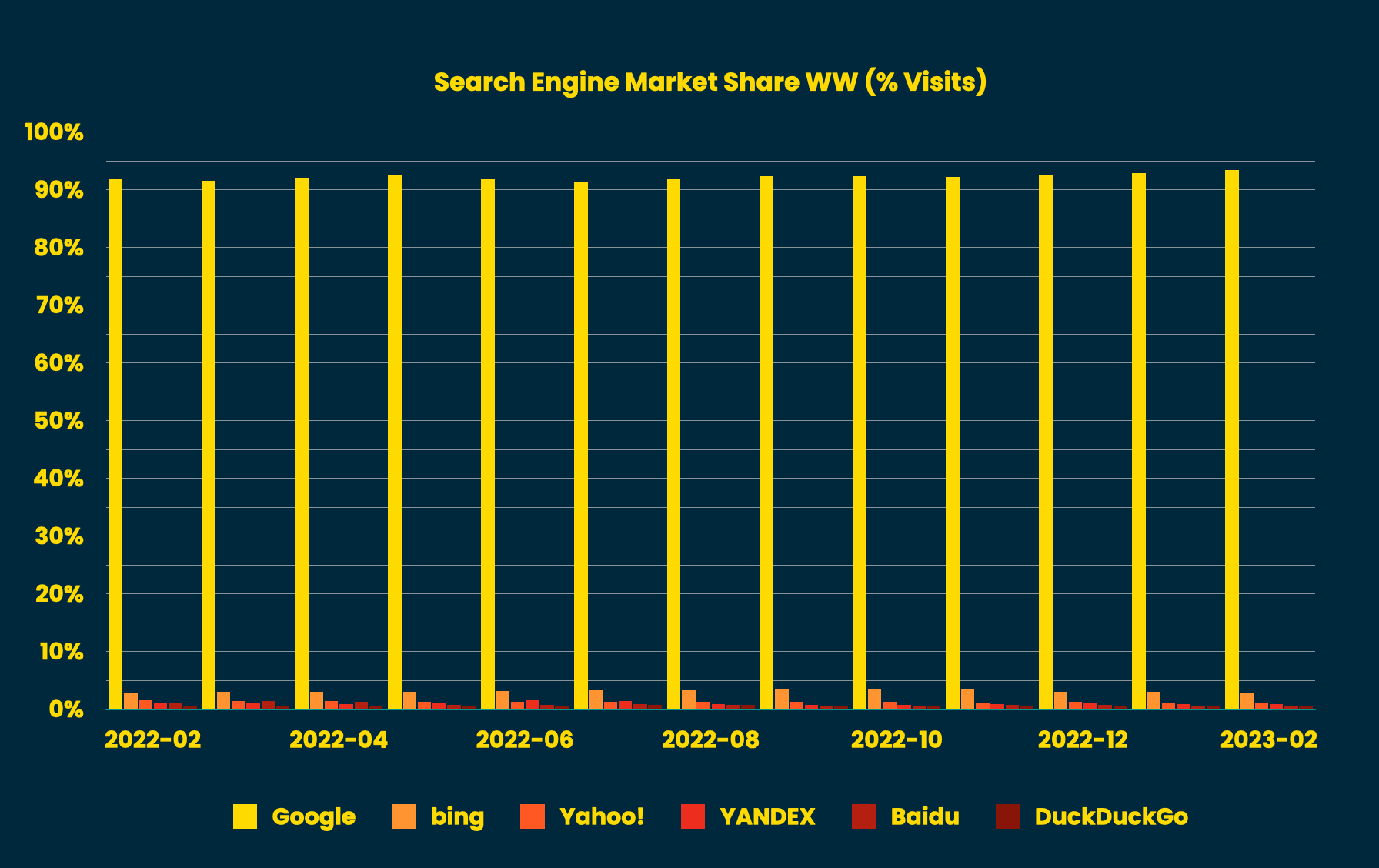
Yandex is the fourth most popular search engine behind Google, Bing, and Yahoo! with the following percentages of the search market as of March 2023: Google at 93.37%, Bing at 2.81%, Yahoo! at 1.13%, and Yandex at 0.85%
(*Statcounter – SEM Market Share Worldwide Feb 23).
Yandex holds a significant market share within the Russian Federation and is also popular in other countries:-
- Belarus: 19.91%
- Tajikistan: 15.77%
- Uzbekistan: 15.35%
- Turkey: 13.41%
- Kazakhstan: 12.44%
- Armenia: 5.78%
The source code leak has been linked to the Russian Federation’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, which may have prompted someone internal to Yandex to leak 45GB of source code onto GitHub. The source code is from February 2022 and July 2022 and was leaked in January 2023.
We’re a Napier SEO agency and we reverse-engineered the source code in February 2023. In our professional opinion, the Yandex source code provides valuable insights into Google ranking factors due to the similarities between RankBrain and MatrixNet, PageRank and Page Rank. Both search engines use personalisation techniques. We estimate that there is a 70% correlation between the Yandex and Google ranking factors.
Search engine ranking factors are used to evaluate a website’s relevance in relation to the search term. The more relevant the webpage, the higher that page will rank for the chosen search term. Google often publishes guidance for quality ratings using E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness – E-A-T was updated to E-E-A-T in Jan 2023) to evaluate webpage ranking factors systems.
We have screen grabs of the source code which highlight the following ranking factors that we’ve discovered in the source code:
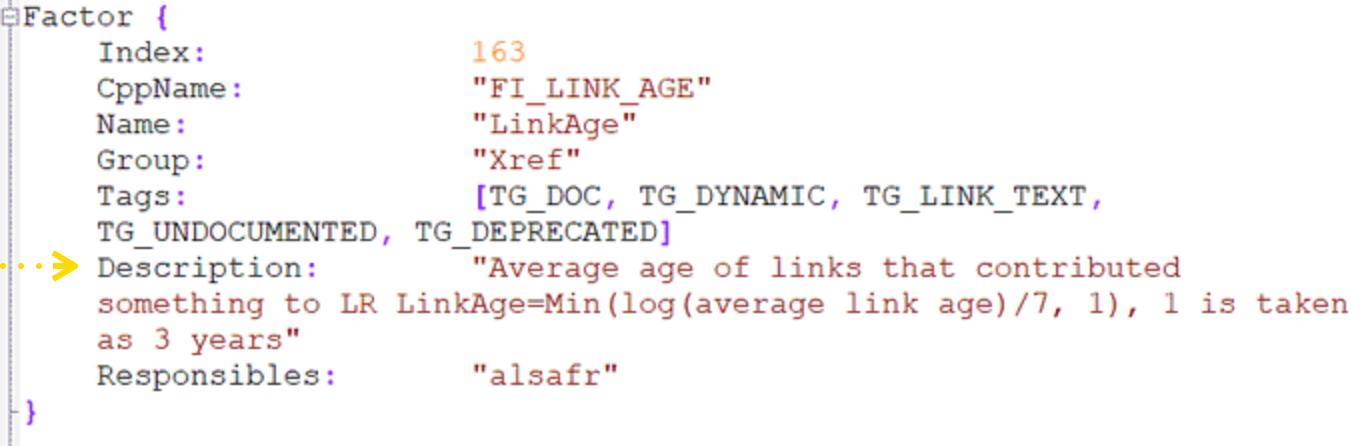
1. Age of Links
Older links are more valuable, as they indicate a long-standing trust and relevance to the website.
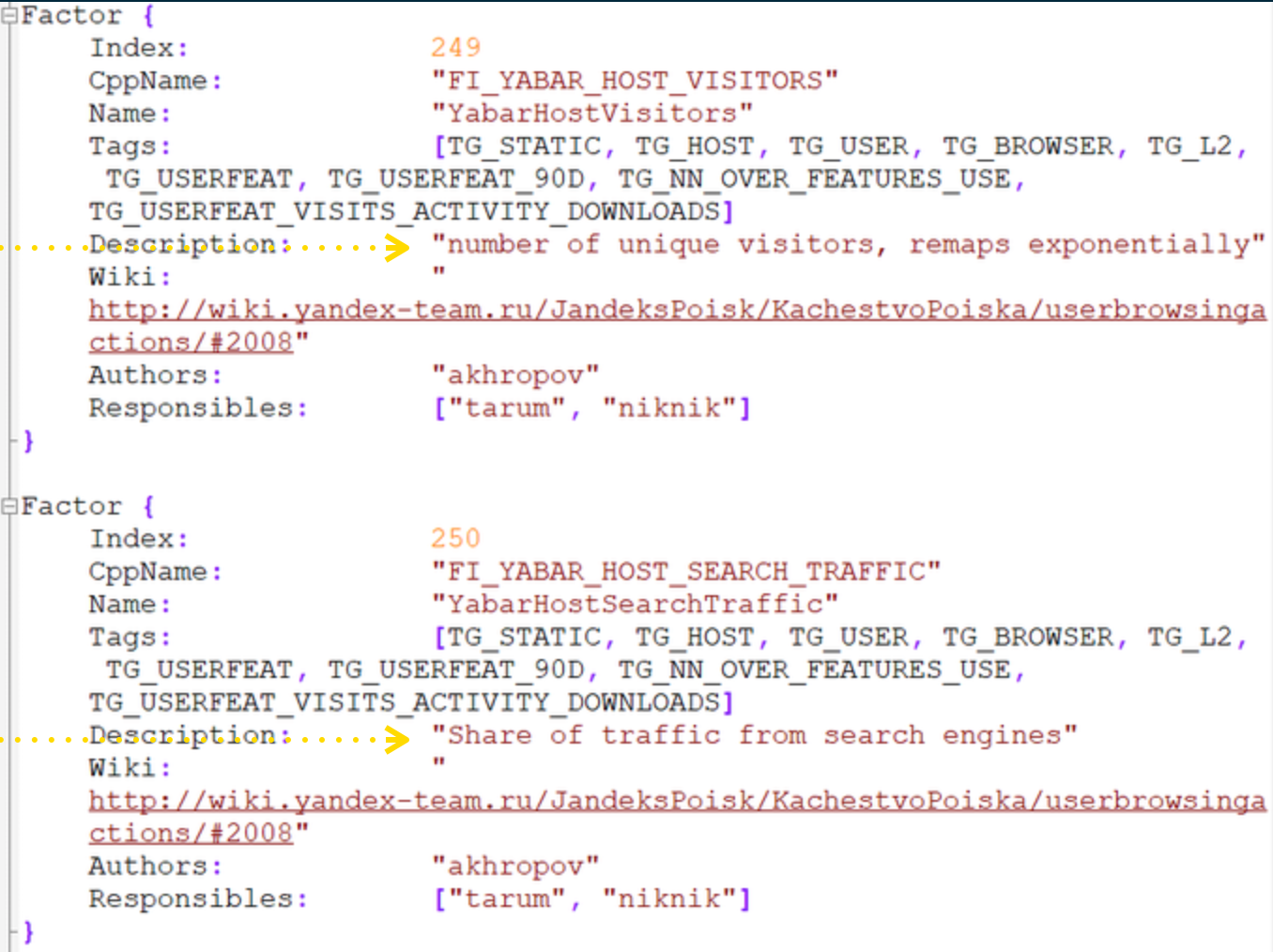
2. Traffic and % of Organic Traffic
Buying PPC traffic affects your ranking. More traffic to your site is seen as a ranking factor. SEO is confirmed (by Yandex) as Pay to Play. We’ve long suspected that this is the case and it’s rewarding to see it confirmed. Naturally – this isn’t purely Paid Search marketing and can relate to any form of paid advertising that results in driving relevant search traffic to your site.
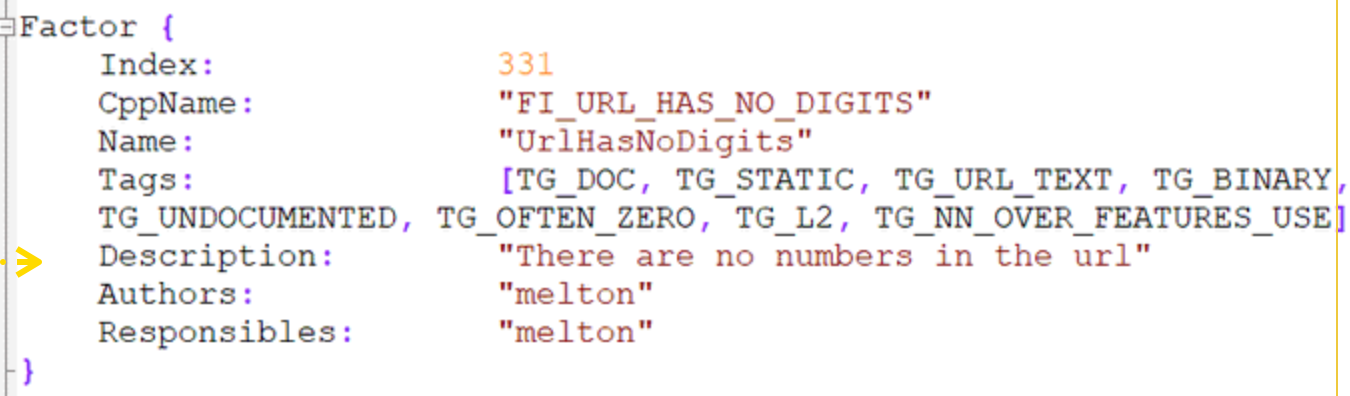
3. Numbers in Your URL are Bad
Having numbers in your URL can negatively impact your ranking, as it may be perceived as less relevant or less user-friendly. This is of particular interest to sites developed in WordPress that use the default upload to a directory containing that organises by month and date.
4. Lots of Slashes in URL
Having too many slashes in your URL structure can also negatively impact your ranking. This is normally indicative of content that has been stored in many sub-directories which causes unnecessary deep indexing by the search engines, such/as/a/long/directory/path/like/this

5. Pessimization means Page Rank of 0
Pessimization refers to the practice of intentionally reducing the quality of a webpage or its content. If a page is identified as pessimized, its Page Rank may be reduced to 0.
This isn’t terribly revelatory – if you intentionally reduce the quality of page to reduce the propensity of being ranked, then this wil be identified and you page won’t rank.

6. Hosting Reliability is a Factor
The reliability of your web hosting provider can impact your search engine ranking. A reliable host ensures better user experience and faster loading times, which are important ranking factors – that’s why we built web-hosting solution specifically for SEO.

7. You Get a Boost if You’re on Wikipedia
if your website happens to be Wikipedia, you’ll get a boost!

8. User Behaviour
Relative CTR, time-on-site, and users visiting the page and completing no action are potential ranking factors. However, these should be taken with a pinch of salt, as user behaviour can be highly variable. It’s also quite telling that bounce-rate has been effectively replaced by engaged user-sessions.
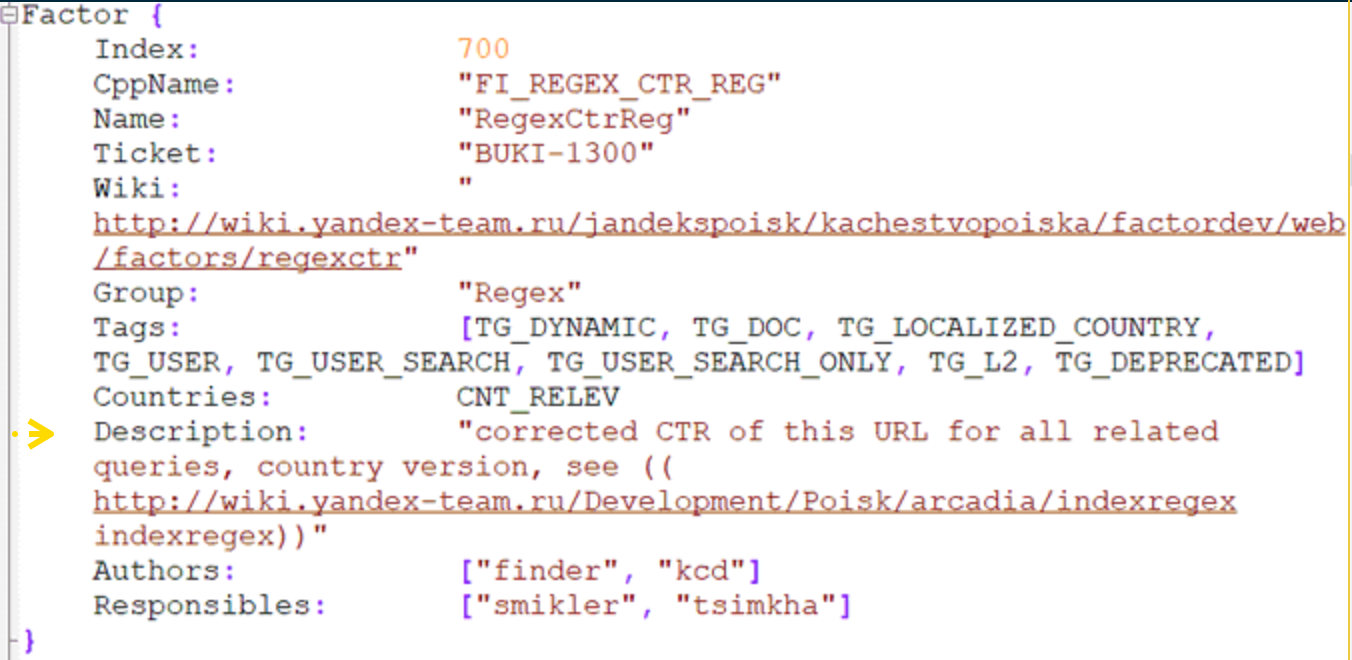
9. Age & Updates
The age of the page and the last time the page was updated are both ranking factors. Regularly updating your content keeps it fresh and relevant, which is important for maintaining a high ranking.
10. Non-Letters in the URL
Using non-letter characters, such as ternary operators, in your URL can negatively impact your ranking, as it may make the URL less readable and user-friendly. We believe this to be mainly where a site is parsing a page function in the address bar – for instance an on-site search query often uses a q=? in the address bar – which is a page that we wouldn’t really want to be indexed, conversely -if you don’t use SEO friendly addresses in content management systems like WordPress, Joomla or Drupal, then expect to penalised.

11. Spamming the URL Field
Using keywords in the URL that do not appear on the page can negatively affect your ranking, as it may be seen as an attempt to manipulate search results.
12. No More Than 3 Consecutive Search Terms in the URL
Specifically, trigrams (three descriptive factors in the URL) should be limited. For example, “/hotels-new-zealand” is good, but “/cheap-hotels-new-zealand-best-deals” is bad.

The insights gained from the reverse engineering the Yandex source code aren’t hugely revolutionary and they mostly represent good website hygiene. The correlation between paid traffic and organic traffic has long been suspected by people working in Google SEO and it’s encouraging to see it finally confirmed by the Yandex source code leak.
We can leverage the insights gained from analysing Yandex’s leaked source code to optimise our Google SEO strategy. Although there may not be a perfect correlation between the ranking factors of both search engines, understanding the similarities and differences can provide valuable insights into how to improve your website’s search engine performance.
The leak of Yandex’s source code has provided a unique opportunity for SEO agencies and digital marketers to gain a deeper understanding of search engine ranking factors. By applying these findings to Google SEO, you can potentially enhance your website’s visibility and performance in search results.
Say hello…
Let’s talk, chat, email, however you like to make things happen.
Call +64(0)2777 666 95 or email Hello@FizzyPop.nz